About Epilepsies
- The epilepsies are a group of heterogenous disorders, due to multiple aetiologies, with onset across all ages, where epileptic seizures are the presenting or the predominant symptom.
- They may have an impact on neurodevelopment, quality of life, education, and/or mortality. Comorbidities (= medical conditions that you have in addition to a primary diagnosis) are frequent. The epilepsies affect at least 6 million people in Europe; 65% individuals will respond to antiseizure drugs or enter spontaneous remission in their lifetime. Of the remaining two million, one third could benefit from a well conducted pre-surgical evaluation and epilepsy surgery. In addition, a significant number will have presented with a distinctive rare epilepsy syndrome/disease for which the prognosis for control of seizures and neurodevelopmental outcome is extremely poor. In short, rare and complex epilepsies affect nearly 5 people in 10,000 of the general population.
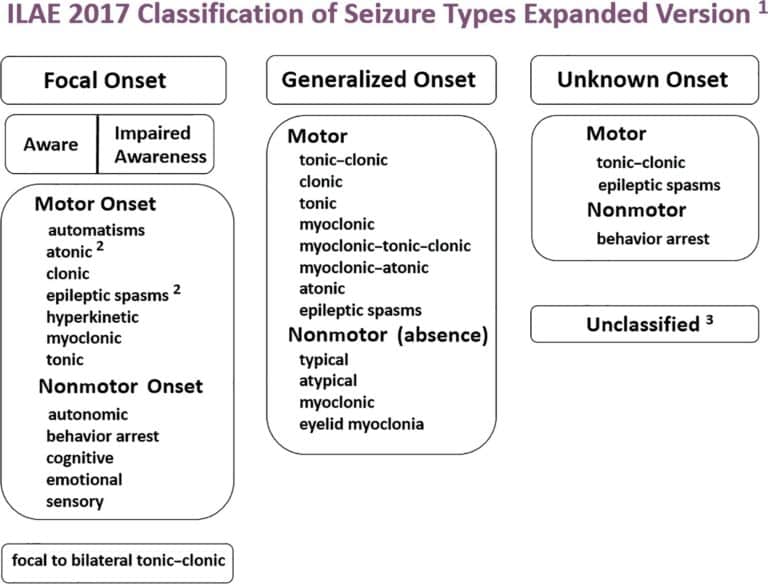
Operational classification of seizure types by the International League Against Epilepsy: Position Paper of the ILAE Commission for Classification and Terminology
Epilepsia, Volume: 58, Issue: 4, Pages: 522-530, First published: 08 March 2017, DOI: (10.1111/epi.13670)
Epilepsy is not “a single disease”. With careful observation and description of the clinical manifestations (epileptic seizures and other neurological/somatin symptoms) combined to an optimal use of diagnostic tools, an increasing number of individual diseases and syndromes have emerged. Age at onset is highly variable.
In addition to a thorough clinical examination and detailed history taking, the investigational tools include video-electroencephalography and advanced neuro-diagnostics including: high resolution MRI often combined to functional neuro-imaging, genetic screening, advanced metabolic diagnostics and a neuro-psychological evaluation.
- The needs for cross border healthcare for patients with rare and complex epilepsies were recognized by the WHO (Resolution WHA73.10 on Nov 12, 2020) and approved as an Intersectoral Global Action Plan on Epilepsy and other Neurological disorders (IGAP). The European Union had already recognized the specific needs for rare and complex diseases and particularly of the epilepsies. Starting 2017, the EU provided the legal grounds and funding which led to the establishment of 24 ERNs from which one specifically targeted Rare and Complex Epilepsies (EpiCARE).
- The main challenge when developing a trans-boarders EU health care network for rare and complex epilepsies derives from the nature of the area of disease. Indeed, the epilepsies are considered a spectrum disorder because of the different causes, different seizure types, its ability to vary in severity and impact from person to person, and its range of co-existing conditions. There are also, many different types of epilepsy, resulting from a variety of causes. However, all types of epilepsies initially manifest themselves with epileptic seizures, a common symptom not always allowing an easy recognition of a potentially rare or complex epilepsy-disease. This is why the ERN EpiCARE serves as the backbone for the development of competent reference networks at a national level.

Methodology for classification and definition of epilepsy syndromes with list of syndromes: Report of the ILAE Task Force on Nosology and Definitions
Epilepsia, Volume: 63, Issue: 6, Pages: 1333-1348, First published: 03 May 2022, DOI: (10.1111/epi.17237)
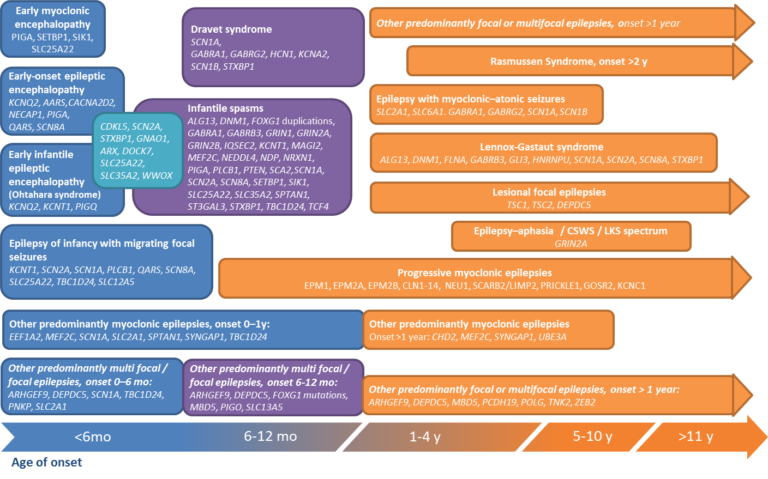
EpiCARE is dealing with more than 160 rare forms of epilepsy, a number steadily augmenting as new forms of genetic epilepsies are identified every year. To those should be added the highly complex cases of focal epilepsies that could benefit from a surgical treatment. This treatment option can be proposed to patients concerned only after a long pre-surgical evaluation process assessing eligibility to a surgical treatment, an evaluation that can only be performed by multidisciplinary medical and surgical hospital-based teams. Early screening and, whenever possible, early diagnosis and the choice of the most appropriate treatments (medical or surgical) are of utmost importance.
You will find below a list of most of the rare and complex syndromes and diseases with epilepsy the ERN EpiCARE is working on.
- The Nosology publications produced by the International League Against Epilepsy, with contributions from EpiCARE medical teams, provide a comprehensive overview of our current state of knowledge, a constantly evolving field.
- Find out more on epilepsy.
| Related Rare or Complex Disease(s), Condition(s) | |
|---|---|
| Genetic epilepsies |
• 15q13.3 microdeletion syndrome • 1p36 deletion syndrome epilepsy • Alternating Hemiplegia of Childhood (ATP1A3) • Angelman syndrome • CDKL5 (Cyclin-dependent kinase-like) deficiency disorder • Down syndrome related epilepsy • Dravet syndrome (SCN1A) • FOXG1 related epilepsies • Fragile X related epilepsy • GRIN2A related epilepsies • GRIN2B • Inversion-duplication chromosome 15q11 • KCNQ2 related epilepsies • KCNT1 related epilepsies • Pallister-Killian syndrome related epilepsy • Progressive Myoclonic Epilepsies • Protocadherin-19 (PCDH19) related epilepsy • Rett syndrome (MECP2) • Ring Chromosome 14 • Ring Chromosome 20 • SCN1A related epilepsies (other than Dravet Sd) • SCN8A related epilepsies • SYNGAP1 related epilepsies • Genetic epilepsy not otherwise identified |
| Structural epilepsies |
• Angiocentric Glioma (ANET) • Arteriovenous malformation • Astrocytoma Variants • Cerebellar hamartoma • Cerebral Angioma with epilepsy • Dysembryoplastic Neuroepithelial Tumor (DNET) • Focal Cortical dysplasias • Ganglioglioma (GG) • Hemimegalencephaly • Hippocampal Sclerosis • Hypothalamic Hamartoma • Incontinentia Pigmenti • Ito Hypomelanosis • Lissencephaly • Neurofibromatosis type 1 • Periventricular Nodular Heterotopia • Polymicrogyria • Stroke (Haemorrhagic) • Stroke (Ischemic) • Sturge Weber syndrome • Subcortical band heterotopias • Tuberous sclerosis Complex • Lesional (Structural) epilepsy not otherwise identified |
| Infectious epilepsies |
• Herpes simplex encephalitis • CMV encephalitis • Other Infectious-related encephalitis with epilepsy |
| Immune epilepsies |
• Acute Febrile Epileptic Encephalopathy • Anti-NMDA receptor limbic encephalitis • Autoimmune encephalitis • Febrile Infection-Related Epilepsy Syndrome (FIRES) • GABA-A receptor antibody mediated immune epilepsy • GABA-B receptor antibody mediated immune epilepsy • GAD- antibody mediated immune epilepsy • Glycine receptor antibody mediated immune epilepsy • MOG-antibody mediated immune epilepsy • NORSE • Rasmussen encephalitis • Non-specified antibody related immune epilepsy • Other antibody related immune epilepsies |
| Surgically treatable epilepsies, subject to a pre-surgical evaluation |
• Focal cortical dysplasias • Hypothalamic Hamartoma • Hemimegalancephaly • Low-grade developmental and epilepsy associated brain tumors (LEAT) • Cerebral cavernous malformations • MTLE with hippocampal sclerosis • Sturge-Weber syndrome • Other lesional (structural) epilepsies |
| Syndromic epilepsies |
• Self-Limited Neonatal and Infantile Epilepsies • Developmental and Epileptic Encephalopathy with Spike-Wave Activation in Sleep (D/EE-SWAS) • Drug-Resistant Adolescent Absence Epilepsy • Drug-resistant Childhood Absence Epilepsy • Drug-resistant Juvenile Myoclonic Epilepsy • Early-infantile Developmental and Epileptic Encephalopathy • Epilepsy of Infancy with Migrating Focal Seizures • Epilepsy with Generalized Tonic-Clonic seizures only • Epilepsy with Myoclonic Absences (E-MA) • Hemiconvulsion-Hemiplegia-Epilepsy (HHE) • Infantile Spasms syndrome (West syndrome) • Landau-Kleffner syndrome • Lennox-Gastaut syndrome (LGS) • Myoclonic Atonic epilepsy (MAE) • Photosensitive Occipital Lobe Epilepsy (POLE) Epilepsy with Eyelid Myoclonia (E-EM) • Sleep-related Hypermotor Epilepsies |
| Metabolic epilepsies |
• Pyridoxine dependent seizures (ALDH7A1) • Inborn Errors of Creatine Metabolism (including GAMT) • Molybdenum Cofactor Deficiency • POLG related epilepsies • Glucose transporter type 1 deficiency • Biotinidase deficiency • Mitochondrial diseases with epilepsy • Metabolic epilepsy not otherwise identified |
| Acute neonatal seizures |
• Neonatal hypoxic and ischemic brain injury • Paediatric arterial ischemic stroke |
| Metabolic neonatal seizures |
• Acute neonatal citrullinemia type 1 • Neonatal glycine encephalopathy • Pyridoxal phosphate-responsive seizures • Pyridoxine-dependent epilepsy |
| Syndromic neonatal seizures |
• Self-Limited Neonatal Epilepsies (Familial or not) • Other Neonatal Epilepsies |
| Status epilepticus |
• New-onset refractory status epilepticus (NORSE) • Acute encephalopathy with Inflammation-mediated status epilepticus • Continuous Spike-Waves during Slow Sleep • Febrile Infection-Related Epilepsy Syndrome (FIRES) • Non-Convulsive Status Epilepticus |

