European Consortium for Epilepsy Trials
Why a European Consortium for Epilepsy Trials (ECET)

Well-designed clinical trials are essential to provide the evidence needed for rational treatment choices. Clinical trials of antiseizure treatments conducted in the past have many shortcomings, and there is a lack of randomized trials in the majority of epilepsy syndromes. There is a need for stakeholders to promote high quality trials in epilepsy, ideally through establishment of international collaborative networks of qualified investigators.
Similar issues are to be considered when designing and performing trials within the epilepsy-surgery indications and outcomes as well as for upcoming gene therapies. Feasibility studies for the selection of investigating centres must be based on sound scientific criteria rather than technical issues. The selection of centres with expertise in rare and complex epilepsies is essential.
Based on these premises, a group of European clinical investigators with a special interest in the treatment of the epilepsies established a collaborative group named European Consortium for Epilepsy Trials (ECET) with the goal of promoting and improving the quality of collaborative epilepsy trials in Europe, in both adults and children.
What is ECET?
The European Consortium for Epilepsy Trials (ECET) Ltd. represents a group of European experts, Doctors in Medicine, with confirmed expertise in designing, advising, and performing clinical trials and research projects in the fields of epilepsy care and treatment.
ECET Ltd. is formally operating within the framework of Epilepsy Alliance Europe (EAE), a non-for-profit organization that brings together European professional and lay stakeholders associated with the International League Against Epilepsy (ILAE) and with the International Bureau for Epilepsy (IBE).
The main objectives of Epilepsy Alliance Europe are:
- Promote research into the epidemiology, causes, diagnosis, treatment and prevention of epilepsy and its comorbidities.
- Advance and disseminate awareness and knowledge concerning the epilepsies.
- Establish epilepsy as a healthcare priority in Europe.
- Protect the rights of people with epilepsy by fighting stigma, prejudice, and unjustified life restrictions.

ECET centres are selected based on their expertise in clinical trials, both academic and/or supported by Pharma. Most of them are also medical teams accredited by the European Commission as members of the European Reference Network for Rare and Complex Epilepsies, ERN EpiCARE, (see the list of EpiCARE members here). Particularly those involved with the Working Group on Clinical Trials and Targeted Therapies, a driving force for ECET, and experienced investigators based in other countries within the European region.
The consortium delivers a range of support services, including advice and professional expertise on the design and implementation of clinical trials, centralized and standardized adjudication processes, and the organization of educational activities to enhance the skills of researchers, healthcare professionals and patient advocates involved in clinical and research trials.
The Consortium ensures a meaningful representation and strong links between academia, industry, regulatory bodies, and patient advocates to improve the care of patients with epilepsy. ECET also collaborates with the Epilepsy Study Consortium (TESC: https://www.epilepsyconsortium.org) a US based entity with similar aims.
General Data Protection Regulations (GDPR) are respected.
Patient advocates
Their role includes reviewing processes, considering the needs of the epilepsy community as a whole. The patient perspective (such as the risk/benefit balance and the potential burden of trials for caregivers and patients) is paramount to design efficient clinical trials and definition of expected outcomes.
ECET encourages patient representatives’ involvement in research, as they provide a unique perspective on the unmet needs of patients and their caregivers.
ECET's services
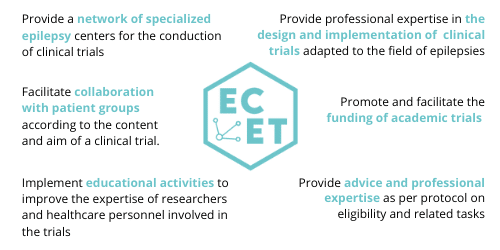
ECET Organisation
ECET is governed by Prs. Alexis Arzimanoglou and Eugen Trinka, with Pr. Reetta Kälviäinen as the treasurer, and Pr. Philippe Ryvlin as secretary.
ECET Project Manager : Mrs. Sébile TCHAICHA.

Eugen Trinka
Chair

Alexis Arzimanoglou
Co-chair

Reetta Kälviäinen
Treasurer

Philippe Ryvlin
Secretary

Sébile Tchaicha
Project manager
Scientific Advisory Committee:
- Stéphane AUVIN (France)
- Andreas BRUNKLAUS (UK)
- Valentina DE GIORGIS (Italy)
- Nicolas GASPARD (Belgium)
- Floor JANSEN (The Netherlands)
- Reetta KALVIAINEN (Finland)
- Lieven LAGAE (Belgium)
- Ronit PRESSLER (UK)
- Philippe RYVLIN (Switzerland)
- Rohit SHANKAR (UK)
- Nicola SPECCHIO (Italy)
- Bernhard STEINHOFF (Germany)
- Pasquale STRIANO (Italy)
- Adam STRZELCZYK (Germany)
- Rainer SURGES (Germany)
- Vicente VILLANUEVA (Spain)
Ex Officio members,
- Pr. Helen CROSS (ILAE President)
- Pr. Jacqueline FRENCH (Epilepsy Study Consortium)
- Pr. Emilio PERUCCA (Founding member and Honorary Consultant)
If you are a medical team with recognized expertise in clinical trials, wishing to join ECET , or an industry professional / investigator wishing to use ECET services, please do not hesitate to contact Sebile Tchaicha, ECET Project manager.

Experts from these institutions contribute to ECET activities:
- Allgemeines Krankenhaus Wien/Medizinische Universität Wien, Vienna, Austria
- Christian Doppler Medical Centre, Paracelsus Medical University and Centre for Cognitive Neuroscience, Salzburg, Austria
- University Hospitals, Leuven, Belgium
- Hôpital Universitaire des Enfants Reine Fabiola (HUDERF)- Brussels Rare and Complex Epilepsies Consortium BRACE, Belgium
- Hôpital ERASME – Brussels Rare and Complex Epilepsies Consortium BRACE, Belgium
- UHC Sestre milosrdnice, Zagreb, Croatia
- University Hospital Centre Zagreb and School of Medicine, University of Zagreb, Referral Centre of the Ministry of Health of the Republic of Croatia for Epilepsy, Croatia
- The Cyprus Institute of neurology and genetics, Cyprus
- Brno Epilepsy Center (St Anne university for adult part and University Hospital Brno for pediatric part), Czech Republic
- Motol University Hospital, Czech Republic
- University Hospital Rigshospitalet, Denmark
- Children’s Clinic of Tartu University Hospital, Estonia
- Epilepsy Center, Kuopio University Hospital, Finland
- Oulu University Hospital, Pediatric Neurology Unit (Helsinki -Oulu ERNEpi Consortium), Finland
- Helsinki University Hospital (Helsinki -Oulu ERNEpi Consortium), Finland
- CHU Lille, France
- Necker Enfants Malades Hospital, Paris, France
- HCL – Hôpital neurologique Lyon, France
- EPIRARES Consortium (Paris-Robert Debré; Rothschild; Salpêtrière), AP-HP, France
- Epilepsy Dpt. University Hospitals of Marseille, AP-HM, France
- Hospices Civils de Lyon, France
- Epilepsy Centre at the University Clinic in Tbilisi, Georgia
- University Berlin Charite, Germany
- Department of Epileptology, University Hospital Bonn, Germany
- Epilepsy Dpt. Universitätsklinikum Tübingen, Germany
- Centre for Paediatrics and Adolescent Medicine, University Hospital Heidelberg, Heidelberg, Germany
- National Institute of Mental Health, neurology and Neurosurgery
Infant Research Centre, Hungary - Irish Centre For Fetalpediat and Neonatal Translational Research, Cork University Maternity Hospital, Ireland
- IRCCS Istituto delle Scienze Neurologiche, Azienda USL di Bologna, Ospedale Bellaria, Italy
- ASST Santi Paolo Carlo-San Paolo Hospital, University of Milan, Italy
- Claudio Munari Epilepsy Surgery Centre, Niguarda Hospital, Milano Italy
- Fondazione IRCCS Istituto Neurologico Besta, Milan, Italy
- Agostino Gemelli University Policlinic, Rome, Italy
- Azienda Ospedaliero-Universitaria Meyer, Firenze, Italy
- Department of Neuroscience at Bambino Gesù Children’s Hospital, Rome, Italy
- Fondazione Mondino, Italy
- AOUI di Verona, Unità Operativa Complessa (UO) di Neuropsichiatria Infantile, Verona, Italy
- IRCCS Instituto Giannina Gaslini, Genova, Italy
- Children’s clinical university hospital, Latvia
- Vilnius University hospital Santaros Clinics, Lithuania
- Hospital of Lithuanian University of Health Sciences, Lithuania
- Mater Dei Hospital, Malta
- University Medical Center Utrecht (UMCU), The Netherlands
- National Centre for epilepsy, Norway
- The Children’s Memorial Health Institute, Warsaw, Poland
- Medical University of Gdańsk, Poland
- Instytut Centrum Zdrowia Matki Polki, Poland
- Centro de Referência para Epilepsias Refratárias. Hospital de Santa Maria – Centro Hospitalar Universitário Lisboa Norte, Portugal
- Centro Hospital Universitário do Porto, Portugal
- Centro Hospitalar e Universitário de Coimbra, Portugal
- Ljubljana University Medical Centre, Dpts. of Child, Adolescent and Developmental Neurology & Department of Neurology, Slovenia
- Queen Elizabeth University Hospital – Glasgow, Scotland
- Hospital Clinic Barcelona, Spain
- Hospital Sant Joan de Déu, Barcelona, Spain
- Hospital Universitario y Politecnico La Fe Valencia, Spain
- University of Gothenburg, Sahlgrenska, Sweden
- Centre Hospitalier Universitaire Vaudois – Lausanne, Swizerland
- John Radcliffe Hospital/University of Oxford, UK
- Great Ormond Street Hospital, London, UK
- University College London Hospitals NHS Foundation Trust, UK
To learn more about ECET and the challenges of epilepsy trials in Europe, watch this webinar by Julius Clinical.
During this webinar, hosted by Dr. Lieza G. Exalto, Prof. Jacqueline French, Prof. Alexis Arzimanoglou and Prof. Eugen Trinka discussed:
> Experiences of the US Epilepsy Consortium
> What is the role of European Reference Network EpiCARE in Epilepsy Trials
>The added value of the European Consortium for Epilepsy Trials (ECET)
